The Andromeda Galaxy: A Cosmic Neighbor
The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as Messier 31 (M31), is one of the most captivating celestial objects visible in the night sky. Located approximately 2.5 million light-years from Earth, it is the closest spiral galaxy to our own Milky Way and offers a glimpse into the dynamic and interconnected nature of the universe.
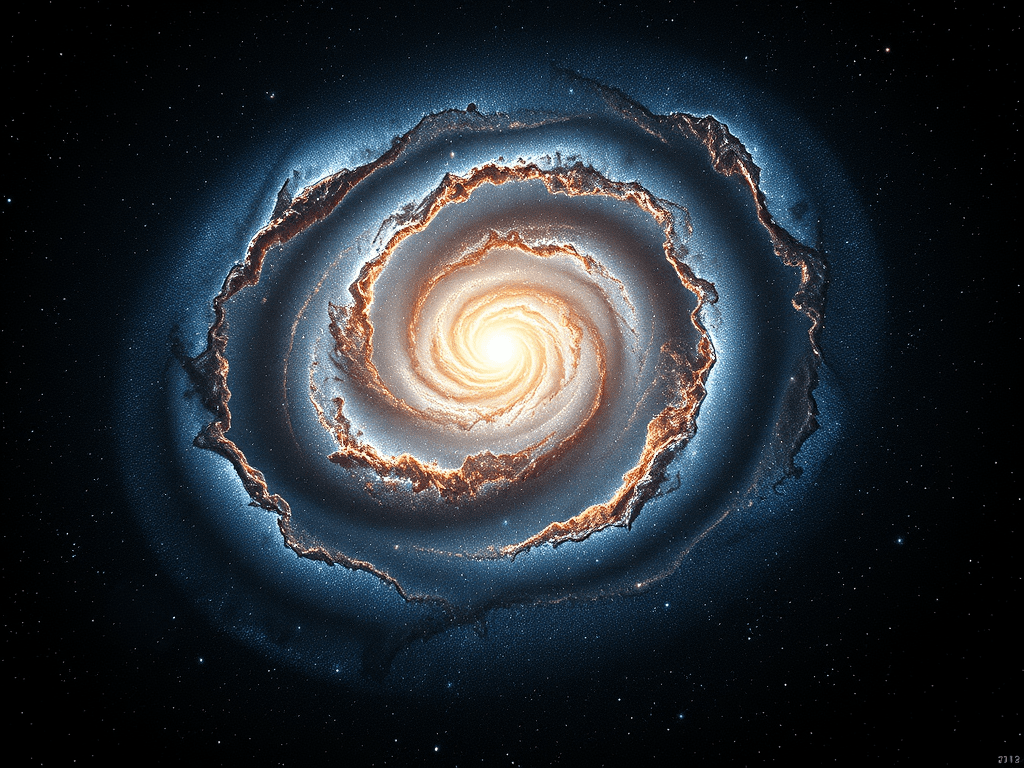
A Spiral Marvel
Andromeda is a massive spiral galaxy, similar in structure to the Milky Way. It spans about 220,000 light-years in diameter, making it over twice as large as our galaxy. With a stellar population estimated at one trillion stars, Andromeda significantly surpasses the Milky Way’s star count. Its iconic spiral arms, laden with clusters of young, luminous stars, are a testament to its ongoing star formation and cosmic activity.
A View from Earth
Andromeda is one of the brightest objects in the night sky, visible to the naked eye from dark-sky locations. Its elongated, misty appearance makes it a favorite target for stargazers and astrophotographers alike. The galaxy can be found in the Andromeda constellation, best observed in the Northern Hemisphere during autumn.
A Future Collision
One of the most intriguing aspects of Andromeda is its impending collision with the Milky Way. Traveling toward us at a speed of about 110 kilometers per second, Andromeda and the Milky Way are destined to merge in approximately 4.5 billion years. This cosmic encounter will result in the formation of a new galaxy, often dubbed “Milkomeda” by astronomers.
Studying Andromeda
As the closest large galaxy, Andromeda serves as a natural laboratory for understanding galactic formation and evolution. Astronomers study its composition, structure, and motion to gain insights into the dynamics of spiral galaxies. Observations of Andromeda’s central supermassive black hole, its satellite galaxies, and its rich halo of stars and dark matter have contributed significantly to our knowledge of the cosmos.
A Connection to the Past
Andromeda’s light carries the history of its ancient stars, some of which are over 10 billion years old. This galaxy has likely undergone numerous mergers and interactions with smaller galaxies, shaping its current form. Its diverse star populations and vast star-forming regions provide clues about its turbulent past and ongoing evolution.
A Beacon of Wonder
The Andromeda Galaxy inspires awe and curiosity, reminding us of the vastness of the universe and our place within it. Whether you view it through a telescope, capture its beauty in photographs, or explore its mysteries through research, Andromeda stands as a timeless symbol of cosmic exploration and discovery.
Leave a comment